1. Introduction: The Heat Behind the Hype
Everyone wants a metabolic spark — something that makes fat loss easier, faster, and more forgiving.
That’s exactly what thermogenic fat burners promise.
But the supplement aisle is crowded with bold claims, aggressive marketing, and very little context.
So let’s start with the real question:
Do fat burners actually burn fat — or are they just expensive stimulants?
To answer that honestly, we need to step away from marketing language and look at biology, chemistry, and clinical reality.
If you’re new to the fundamentals of fat loss, start here first:
👉 Ultimate Guide to Sustainable Weight Loss Methods
https://thehealthknowledgebase.com/weight-loss/sustainable-weight-loss-guide/
This article focuses on one specific tool: thermogenics — what they do, what they don’t do, and who they are (and are not) right for.
2. The Biology of Burning: What Is Thermogenesis?
Thermogenesis is the process by which your body produces heat by burning energy.
It is a normal, continuous process — not something supplements invented.
The Three Primary Sources of Thermogenesis
1. Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
Energy burned at rest to keep you alive:
- Breathing
- Organ function
- Brain activity
BMR accounts for 60–70% of daily calorie burn.
2. Thermic Effect of Food (TEF)
Energy used to digest and process food.
- Protein has the highest TEF
- Ultra-processed foods have the lowest
3. Activity-Based Thermogenesis (EAT + NEAT)
- EAT: Exercise activity
- NEAT: Daily movement (walking, standing, chores)
This category is the most flexible — and the most influenced by lifestyle.
Where Supplements Fit In
Thermogenic supplements attempt to chemically stimulate these systems, primarily by:
- Increasing nervous system activity
- Elevating stress hormones
- Encouraging greater energy expenditure
They do not create new fat-burning pathways.
They amplify existing ones — temporarily.
3. How “Fat Burners” Work (The Scientific Mechanisms)
Thermogenic supplements rely on a few core biological mechanisms.
1. Lipolysis Stimulation
Lipolysis is the process of breaking stored fat into free fatty acids that can be used as fuel.
Certain compounds:
- Increase adrenaline and noradrenaline
- Signal fat cells to release stored energy
This does not guarantee fat loss — the energy still must be used.
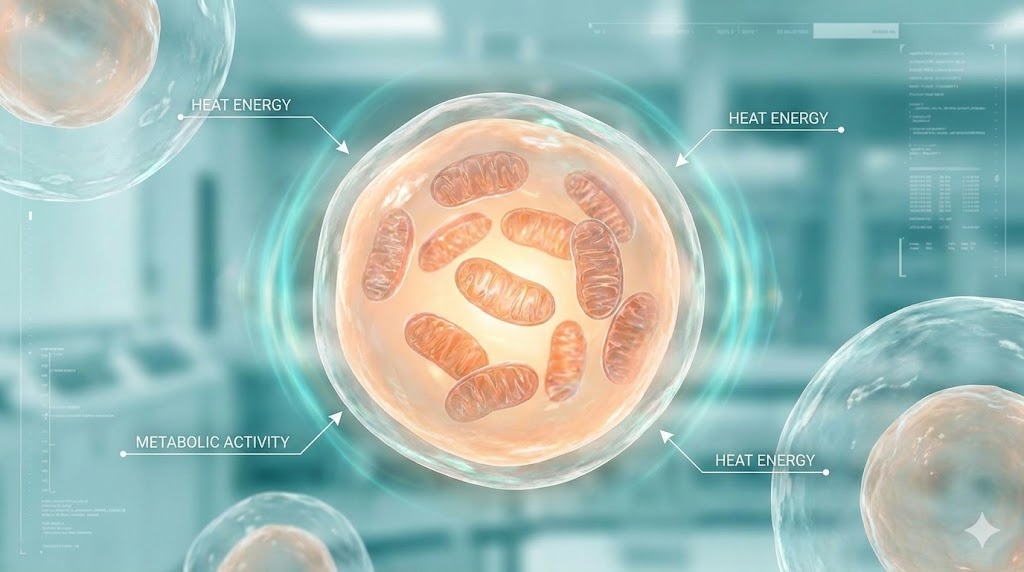
2. Uncoupling Proteins (UCPs)
Some compounds increase the activity of uncoupling proteins inside mitochondria.
This causes:
- Less energy stored as ATP
- More energy released as heat
Result: slightly higher calorie burn, lower efficiency.
3. Adrenaline Mimicry
Most thermogenics work by mimicking a stress response.
This “fight or flight” signal:
- Raises heart rate
- Increases alertness
- Mobilizes stored energy
This is also why side effects occur.
4. Common Thermogenic Ingredients vs. Science
| Ingredient | Mechanism | Evidence Level | Verdict |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caffeine | Increases adrenaline & nervous system activity | High | Reliable, dose-dependent |
| Green Tea (EGCG) | Enhances fat oxidation enzymes | Moderate | Best combined with caffeine |
| Capsaicin | Increases heat production | Moderate | Small but measurable effect |
| Yohimbine | Blocks fat-storage receptors | Low / Niche | Potent but high risk |
Key takeaway:
Most results come from caffeine, not exotic ingredients.
5. The Clinical Reality: Results You Can Actually Expect
This is where expectations matter.
The “5% Rule”
Even effective thermogenics typically increase total daily calorie burn by 3–5%.
For most people, that equals:
- 50–150 extra calories per day
Helpful — but not transformational.
Tolerance & Diminishing Returns
Your nervous system adapts quickly.
Over time:
- Stimulant effects weaken
- Higher doses are needed
- Side effects increase
This limits long-term usefulness.
The “Safety Net” Fallacy
Fat burners do not:
- Cancel overeating
- Offset poor sleep
- Fix inconsistent training
They amplify habits — good or bad.
6. Are Fat Burners Right for You? (Self-Assessment)
Good Candidate
You may benefit if you:
- Already maintain a calorie deficit
- Train consistently
- Sleep well
- Want a short-term performance edge
Avoid If You:
- Have heart conditions or high blood pressure
- Are prone to anxiety or panic attacks
- Struggle with sleep
- Are new to weight loss fundamentals
For beginners, supplements often mask problems instead of solving them.
7. Risks_toggle and Side Effects
Cardiovascular Strain
- Elevated heart rate
- Increased blood pressure
- Palpitations
Nervous System Stress
- Anxiety
- Irritability
- “Crash” fatigue
Digestive Irritation
- Nausea
- Reflux
- Gut discomfort (especially capsaicin-heavy formulas)
These risks scale with dose and stacking.
8. Conclusion: Tool or Trap?
Thermogenics are tools — not solutions.
They work best when:
- Diet is locked in
- Training is consistent
- Sleep is prioritized
They work worst when used as shortcuts.
Final advice:
Before reaching for a fat burner, maximize:
- Protein intake
- Daily movement
- Sleep quality
Those alone outperform most supplements.
FAQ’s
1. What are thermogenic supplements?
Thermogenic supplements are products designed to increase heat production in the body by stimulating the nervous system and metabolism. They aim to slightly raise daily calorie expenditure, often through stimulant-based ingredients like caffeine.
2. Do fat burners actually burn body fat?
Fat burners do not directly “burn” fat. They may increase energy expenditure or fat mobilization, but fat loss still depends on maintaining a calorie deficit. Supplements only support the process.
3. How much weight can thermogenics help you lose?
Most research suggests thermogenics increase daily calorie burn by about 3–5%, which may result in modest fat loss over time when combined with diet and exercise.
4. Are thermogenic supplements safe?
They can be safe for healthy adults when used responsibly, but many contain stimulants that may cause side effects. People with heart conditions, anxiety disorders, or high blood pressure should avoid them unless cleared by a doctor.
5. What is the main ingredient that makes fat burners work?
Caffeine is the most effective and well-studied thermogenic ingredient. Most fat burners rely heavily on caffeine for their metabolic and energy-boosting effects.
6. Can fat burners replace diet and exercise?
No. Fat burners cannot replace a calorie-controlled diet, regular physical activity, or proper sleep. They only amplify existing habits and are ineffective without a solid foundation.
7. Why do fat burners stop working over time?
The body adapts to stimulants through tolerance. Over time, the same dose produces less effect, which is why thermogenics are often less effective long term.
8. Are non-stimulant fat burners better?
Non-stimulant options may reduce side effects, but they usually produce smaller results. Their effectiveness depends heavily on diet consistency and physical activity.
9. Who should avoid thermogenic supplements?
Thermogenics should be avoided by:
- People with cardiovascular conditions
- Those prone to anxiety or insomnia
- Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals
- Beginners who have not established a calorie deficit
10. What should I try before using a fat burner?
Before using thermogenics, prioritize:
- Higher protein intake
- Better sleep quality
- Increased daily movement (NEAT)
- Consistent strength training
These strategies often outperform supplements.