Introduction: The Silent Fire Within
Most people treat weight gain like the main problem. But for many, stubborn weight is the smoke—not the fire.
That “fire” is often chronic, low-grade inflammation: a persistent immune response that quietly disrupts metabolism, blood sugar regulation, thyroid function, and appetite signals. Over time, your body can shift into a state where it struggles to burn fat efficiently, even when you’re doing “everything right.”
This is where the anti inflammatory diet becomes more than a trend. Done properly, it’s a functional nutrition strategy designed to move you from a pro-inflammatory state to a more healing, resilient state—supporting weight loss while also reducing the long-term burden that can contribute to autoimmune flare-ups.
If you’re building your foundation for sustainable fat loss, start here:
Return to the master Weight Loss hub: https://thehealthknowledgebase.com/weight-loss/
Lifelong Habits and the Autoimmune “Trigger”
Inflammation rarely appears overnight. It often builds quietly for years—sometimes decades—driven by patterns that are now normalized:
- Ultra-processed foods as the default
- High refined carbohydrate intake with low fiber
- Excess added sugar and sweetened beverages
- Frequent fried foods and heavily refined oils
- Chronic under-sleeping and high stress
- Low intake of omega-3 fats, minerals, and phytonutrients
The cumulative effect
When your diet is consistently low in nutrients and high in inflammatory inputs, the immune system never fully “powers down.” This can elevate markers like CRP (C-reactive protein) and keep the body in a state of metabolic friction.
The breaking point
Under constant immune stress, the body may become more reactive. In susceptible individuals, that can contribute to an immune system that misfires—struggling to differentiate “self” from “invader,” and driving autoimmune activity.
Common manifestations linked to inflammation
While many factors influence autoimmune conditions (including genetics, environment, infections, and stress), nutrition can strongly affect symptom burden and metabolic resilience:
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: inflammation impacting thyroid function—your metabolic “engine”
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA): systemic inflammation affecting joints and connective tissue
- Psoriasis & lupus: inflammatory immune activity affecting skin and organs
Important note: an anti-inflammatory diet is not a cure for autoimmune disease, but it can be a powerful lifestyle lever that supports symptom management and overall metabolic health.
Why Weight Loss Stalls During Inflammation
When inflammation is high, fat loss often becomes harder—not because you lack discipline, but because your physiology is working against you.
1) Cortisol and insulin push the body toward “storage mode”
Chronic inflammation often coexists with elevated stress signaling. This can promote:
- Higher cortisol, increasing cravings and disrupting sleep
- Reduced insulin sensitivity, making it easier to store calories as body fat
- Increased hunger hormones and reward-driven eating patterns
If stress and sleep are part of your picture, you’ll want this companion article:
The Role of Sleep and Stress in Natural Weight Loss
https://thehealthknowledgebase.com/weight-loss/natural-methods/sleep-stress-weight-loss/
2) The thyroid connection
If thyroid function is impaired—whether clinically diagnosed or suboptimal—your body may reduce metabolic output. When the immune system is inflamed and “busy,” it can affect thyroid signaling pathways, which can impact energy, body temperature regulation, and fat oxidation.
The takeaway: inflammation can slow the very systems required for efficient weight loss, even before lab values look dramatically abnormal.
The Anti-Inflammatory Pantry: Healing Foods
This is the practical side: you don’t need perfection. You need consistent exposure to foods that deliver anti-inflammatory compounds and support the gut, liver, and blood sugar balance.
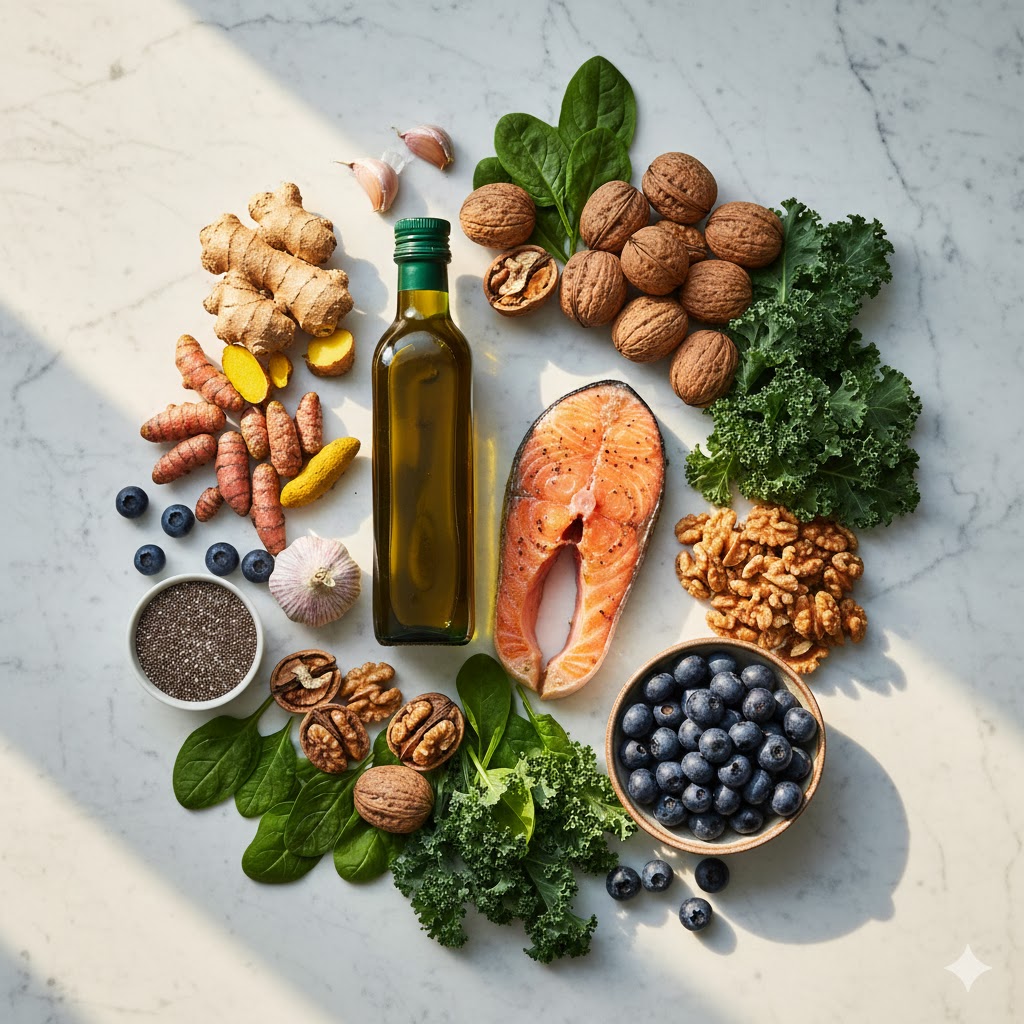
Healthy fats that calm inflammation
- Extra virgin olive oil (EVOO): rich in polyphenols and compounds associated with anti-inflammatory effects (often discussed alongside “oleocanthal”).
- Fatty fish (salmon, sardines, mackerel): provides omega-3s that support a healthier omega-3:omega-6 balance.
Micronutrient powerhouses
- Walnuts, chia seeds, flax: fiber + beneficial fats that support gut and metabolic health
- Leafy greens (spinach, arugula, kale): high nutrient density with low energy density
- Berries (blueberries, blackberries): polyphenols and antioxidants that support cellular resilience
Nature’s pharmacy
- Turmeric (curcumin): widely used for inflammatory support
- Ginger: digestive and anti-inflammatory properties
- Garlic: supports immune balance and cardiovascular health patterns
The mindset win: “Yes” foods that feel like a treat
- Dark chocolate (high cacao): in moderation, can provide polyphenols and can make the plan feel sustainable—key for long-term adherence.
If mornings are when your habits tend to fall apart, pair this blueprint with:
5 Science-Backed Metabolism-Boosting Drinks to Start Your Day
https://thehealthknowledgebase.com/weight-loss/natural-methods/metabolism-boosting-drinks/
Pro-Inflammatory vs. Anti-Inflammatory Swaps
Use this as your “default decision system” at the supermarket.
| Pro-Inflammatory (Avoid) | Anti-Inflammatory (Swap To) | Metabolic Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Refined soybean/corn oils | Extra virgin olive oil | Supports healthier inflammatory markers (e.g., CRP trends) |
| Sugary snacks/candies | Dark berries + high-cacao dark chocolate | Higher polyphenols; steadier appetite signals |
| Processed deli meats | Fatty fish (salmon/sardines) | Better omega-3 intake; supports metabolic flexibility |
| White bread/pasta | Leafy greens + seeds + legumes | More fiber; improved gut and blood sugar support |
Getting Started: The “Add, Don’t Subtract” Method
Most diets fail because they start with punishment.
The simplest way to make an anti inflammatory diet sustainable is to focus on adding healing foods first:
Week 1: Add one anchor meal per day
Pick one meal (often breakfast or lunch) and make it anti-inflammatory by default:
- Eggs + spinach + EVOO drizzle
- Greek-style salad + salmon
- Oats + chia + berries + walnuts
Week 2: Add two “staples” you always keep in the house
Examples:
- EVOO and frozen berries
- Canned sardines and mixed greens
- Turmeric/ginger and garlic
Week 3: Swap one inflammatory item you consume daily
Common high-impact swaps:
- Replace sweetened drinks with water + lemon
- Replace refined snacks with berries + yogurt (or dark chocolate + nuts)
- Replace refined oils with EVOO
Consistency beats intensity
You cannot unwind years of metabolic inflammation in 48 hours. But you can shift your trajectory quickly by consistently stacking anti-inflammatory exposures.
For an execution-ready plan, continue here:
Diet & Nutrition Plans Silo: https://thehealthknowledgebase.com/weight-loss/diet-plans/
Conclusion: Eating for Longevity
An anti-inflammatory diet is not just a weight loss plan—it’s a long-term strategy for metabolic resilience.
When you lower the “silent fire,” you create a body that is more willing to:
- regulate hunger normally
- stabilize blood sugar more effectively
- recover better from workouts
- sleep deeper
- use fat as fuel more efficiently
And if you’re dealing with autoimmune risk factors or symptoms, this blueprint can function like an “insurance policy” for your immune system—because the most powerful daily health decision is often made at the end of your fork.
Return to the master Weight Loss hub:
https://thehealthknowledgebase.com/weight-loss/
FAQs
- What is an anti-inflammatory diet?
An eating pattern that emphasizes whole, minimally processed foods—especially omega-3 fats, fiber, and polyphenol-rich plants—while reducing ultra-processed foods and excess added sugars that can increase inflammatory signaling. - Can an anti-inflammatory diet help with weight loss?
Yes, often indirectly. Lower inflammation can improve appetite regulation, sleep quality, insulin sensitivity, and energy—factors that make a calorie deficit easier to sustain. - Is the Mediterranean diet considered anti-inflammatory?
Commonly, yes. Mediterranean-style eating tends to be rich in olive oil, fish, vegetables, legumes, and fruit—foods associated with healthier inflammatory patterns. - What foods cause the most inflammation?
For many people: ultra-processed foods, sugary drinks, refined snacks, frequent fried foods, and low-fiber diets. Individual triggers vary. - Is gluten inflammatory for everyone?
Not necessarily. Some people feel better reducing gluten, particularly those with celiac disease or sensitivity. For others, overall diet quality matters more than gluten alone. - Does turmeric reduce inflammation?
Turmeric (curcumin) is widely used for inflammatory support. Results depend on dose, consistency, and individual response. It works best as part of a whole-food pattern. - How long does it take to see results?
Many people notice changes in energy, digestion, or cravings within 1–2 weeks. Deeper changes (body composition, labs, symptoms) typically require consistent adherence for several weeks. - Can this diet help Hashimoto’s or rheumatoid arthritis?
It can support symptom management by lowering inflammatory load and improving nutrient intake, but it is not a cure and should complement medical care. - Do I need to cut seed oils completely?
You don’t need perfection. A practical approach is to reduce heavily fried/processed sources while increasing olive oil, fatty fish, nuts, and fiber-rich plants. - What’s the easiest way to start?
Use the “add, don’t subtract” approach: add EVOO, berries, leafy greens, and fatty fish consistently—then swap one processed staple at a time.
Related Articles
Within Diet Plans:
- Beginner’s Guide to Counting Macros for Weight Loss
https://thehealthknowledgebase.com/weight-loss/diet-plans/counting-macros-beginner/ - The 7-Day Anti-Inflammatory Meal Plan for Fast Weight Loss
https://thehealthknowledgebase.com/weight-loss/diet-plans/anti-inflammatory-meal-plan/
Natural Methods:
- The Role of Sleep and Stress in Natural Weight Loss
https://thehealthknowledgebase.com/weight-loss/natural-methods/sleep-stress-weight-loss/ - 5 Science-Backed Metabolism-Boosting Drinks to Start Your Day
https://thehealthknowledgebase.com/weight-loss/natural-methods/metabolism-boosting-drinks/
Ready to build your anti-inflammatory meal plan?
Explore our full library of meal plans, macro guides, and nutritional strategies designed to support sustainable fat loss, steadier blood sugar, and lower inflammatory load—without extreme restriction.
Next step: pick one plan and follow it for 7 days before you judge results.