The Hidden Engine Behind Metabolic Problems
Insulin resistance is the silent engine powering many of today’s most common health struggles — from stubborn weight gain to rising blood sugar and heart disease.
Most people never hear the term until a doctor mentions “prediabetes.” By then, insulin resistance has often been developing quietly for years.
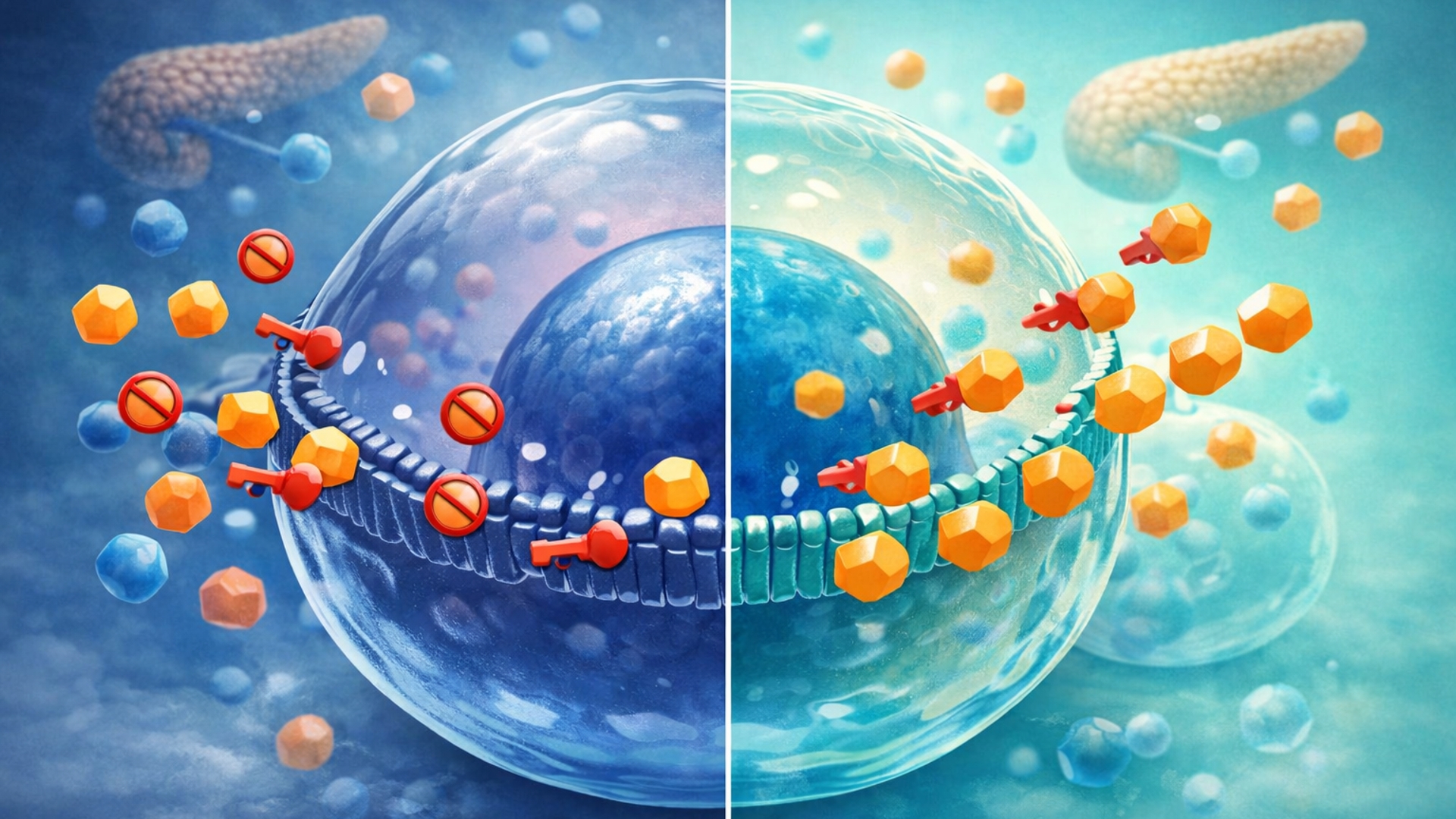
To understand insulin resistance, it helps to use a simple analogy:
- Insulin is the key
- Your cells are the lock
- Glucose is the fuel
In a healthy system, insulin unlocks the cell so glucose can enter and be used for energy.
With insulin resistance, the lock becomes jammed. The key still works — but it takes more and more force to open the door.
Why does this matter?
Because insulin resistance sits at the crossroads of:
- Type 2 diabetes
- Abdominal weight gain
- Cardiovascular disease
- Fatigue and brain fog
This guide explains how to recognize insulin resistance early — and how to fix it naturally.
What Exactly Is Insulin Resistance?
The Science (Simplified)
Every time you eat carbohydrates, they break down into glucose. That glucose enters your bloodstream and must move into cells to be used.
The pancreas releases insulin to make this happen.
In insulin resistance:
- Cells stop responding efficiently to insulin
- The pancreas compensates by releasing more insulin
- Blood sugar may remain “normal” temporarily
- Insulin levels stay chronically elevated
This creates a dangerous condition known as hyperinsulinemia — high insulin levels without obvious symptoms.
Why High Insulin Comes Before High Blood Sugar
Many people believe diabetes starts with high glucose. In reality, high insulin usually comes first.
Years of elevated insulin eventually overwhelm the system, causing blood sugar to rise. By the time glucose numbers are flagged, insulin resistance has already taken hold.
The Vicious Cycle
Insulin resistance feeds itself:
High insulin → increased fat storage
More fat (especially visceral fat) → more insulin resistance
More resistance → even higher insulin levels
Unless interrupted, this cycle continues silently.
For a broader overview of how insulin fits into metabolic health, see the pillar guide:
👉 https://thehealthknowledgebase.com/blood-sugar/management-guide/
Common Symptoms: The Red Flags
Insulin resistance rarely presents as one dramatic symptom. Instead, it shows up as a pattern.
Visible Signs
- Darkened skin patches (acanthosis nigricans), especially around the neck or armpits
- Skin tags
- Increased abdominal fat (“insulin belly”)
Internal Cues
- Strong sugar or carb cravings
- Feeling tired or sleepy after meals
- Brain fog or poor concentration
- Energy crashes in the afternoon
- Difficulty losing weight despite calorie restriction
Blood Work Clues
Standard tests often miss early insulin resistance. Useful markers include:
- HbA1c (average blood sugar over 2–3 months)
- Fasting glucose
- Fasting insulin
- HOMA-IR (a calculation using glucose and insulin)
Understanding what these numbers mean matters.
You can compare healthy ranges here:
👉 https://thehealthknowledgebase.com/blood-sugar/blood-sugar-levels-chart/
The Root Causes: Why Insulin Resistance Develops
Insulin resistance is rarely caused by a single factor. It develops through chronic metabolic overload.
1. Dietary Factors
Frequent intake of refined carbohydrates and liquid sugars — especially fructose — overwhelms the body’s glucose-handling capacity.
Learn how spikes form and how to reduce them:
👉 https://thehealthknowledgebase.com/blood-sugar/preventing-glucose-spikes/
2. Lifestyle Factors
A sedentary lifestyle deprives muscles of regular glucose uptake. Over time, unused glucose lingers in the bloodstream longer.
A simple but powerful intervention is post-meal walking:
👉 https://thehealthknowledgebase.com/blood-sugar/walking-after-meals-benefits/
Sleep deprivation also plays a major role. Even one night of poor sleep reduces insulin sensitivity the following day:
👉 https://thehealthknowledgebase.com/blood-sugar/sleep-and-blood-sugar/
3. Biological Factors
- Genetic predisposition
- Chronic inflammation
- Visceral (deep abdominal) fat
These factors amplify insulin resistance and accelerate progression.
Natural Solutions & Reversal Strategies
The most important message: insulin resistance is not permanent.
1. Nutrition First
Meals built around protein, fiber, and healthy fats slow glucose absorption and reduce insulin demand.
Carbohydrates are not eliminated — they are strategically managed.
Low-glycemic food choices play a key role:
👉 https://thehealthknowledgebase.com/blood-sugar/best-low-gi-foods/
Intermittent fasting may also help some individuals by giving the pancreas a “rest,” when done safely and consistently:
👉 https://thehealthknowledgebase.com/blood-sugar/intermittent-fasting-guide/
2. Movement as Medicine
Muscle contractions allow glucose to enter cells without requiring insulin.
This is why:
- Walking after meals works immediately
- Resistance training improves insulin sensitivity long-term
Movement is not optional — it is metabolic therapy.
3. Stress & Sleep Regulation
Stress hormones like cortisol signal the liver to release glucose, even when energy isn’t needed.
Chronic stress keeps blood sugar elevated regardless of diet:
👉 https://thehealthknowledgebase.com/blood-sugar/stress-and-glucose-levels/
Improving sleep quality restores insulin signaling and reduces cravings.
The “Insider” Edge: Supplements & Support
Lifestyle changes are the foundation — but certain natural compounds may support insulin sensitivity when used responsibly.
Commonly researched ingredients include:
- Berberine
- Cinnamon
- Magnesium
- Chromium
Each works through different metabolic pathways.
Deep-dive ingredient guides and comparisons are available here:
👉 https://thehealthknowledgebase.com/blood-sugar/best-supplements-review/
Always consult a healthcare professional, especially if you are taking medication.
Conclusion: A Problem You Can Fix
Insulin resistance is not a life sentence.
It is a metabolic signal — one that responds remarkably well to:
- Better food structure
- Consistent movement
- Stress reduction
- Improved sleep
Small daily changes compound into dramatic long-term results.
For structured guidance, tools, and next steps, explore the Blood Sugar Hub.
Build a complete plan for stable blood sugar
Visit the Blood Sugar Hub for meal strategies, glucose spike fixes, CGM guides, supplement research, and step-by-step metabolic health resources.
Visit the Blood Sugar Hub →FAQs
- Is insulin resistance reversible?
Yes. With consistent lifestyle changes, insulin sensitivity can improve significantly. - Can you have insulin resistance with normal blood sugar?
Yes. Elevated insulin often appears years before glucose rises. - What is hyperinsulinemia?
It is a condition where insulin levels remain chronically high, often without obvious symptoms. - Does insulin resistance cause weight gain?
Yes. High insulin promotes fat storage and blocks fat burning. - What foods worsen insulin resistance most?
Refined carbohydrates, sugary drinks, and ultra-processed foods. - Does stress alone raise blood sugar?
Yes. Stress hormones trigger glucose release from the liver. - Is intermittent fasting safe for insulin resistance?
It can be helpful for some people when done carefully and consistently. - How long does reversal take?
Early improvements may appear in weeks; deeper reversal takes months. - Do supplements replace lifestyle changes?
No. Supplements support, but do not replace, foundational habits. - Where should I start if I suspect insulin resistance?
Begin with the Blood Sugar Hub for structured, evidence-based guidance:
https://thehealthknowledgebase.com/blood-sugar/