Chronic inflammation is a persistent, low-grade immune response that never fully shuts off.
Unlike acute inflammation—which is protective and temporary—chronic inflammation quietly damages tissues, disrupts hormonal signaling, interferes with metabolism, and accelerates aging.
Most people don’t feel “inflamed.” They experience symptoms that seem unrelated, such as:
- Ongoing joint or muscle pain
- Fatigue that doesn’t improve with rest
- Brain fog or memory lapses
- Digestive discomfort or bloating
- Weight gain resistant to diet and exercise
- Mood changes or anxiety
These symptoms are often treated separately, yet they frequently share one root cause: chronic inflammation.
Acute vs Chronic Inflammation (Why This Matters)
Acute inflammation
- Short-term and protective
- Triggered by injury or infection
- Resolves once healing is complete
Chronic inflammation
- Long-lasting and low-grade
- Often driven by lifestyle and metabolic stress
- Can persist for years without obvious warning signs
Chronic inflammation doesn’t announce itself loudly. It erodes health slowly.
What Causes Chronic Inflammation?
Chronic inflammation is rarely caused by a single factor. It is usually the result of multiple overlapping stressors.
1️⃣ Blood Sugar Instability
Repeated blood sugar spikes trigger inflammatory signaling and insulin resistance.
👉 Deep dive: Metabolic Inflammation
2️⃣ Chronic Stress & Cortisol Dysregulation
Long-term stress keeps the nervous system locked in “fight-or-flight,” increasing inflammatory cytokines.
👉 Deep dive: Brain & Nervous System
3️⃣ Gut Barrier Breakdown
A compromised gut lining allows inflammatory compounds to enter circulation.
👉 Deep dive: Gut Inflammation
4️⃣ Hormonal Imbalance
Inflammation disrupts testosterone, estrogen, and cortisol signaling.
👉 Deep dive: Hormonal & Prostate
5️⃣ Inflammatory Diet Patterns
Ultra-processed foods, seed oils, excess sugar, and alcohol fuel chronic inflammation.
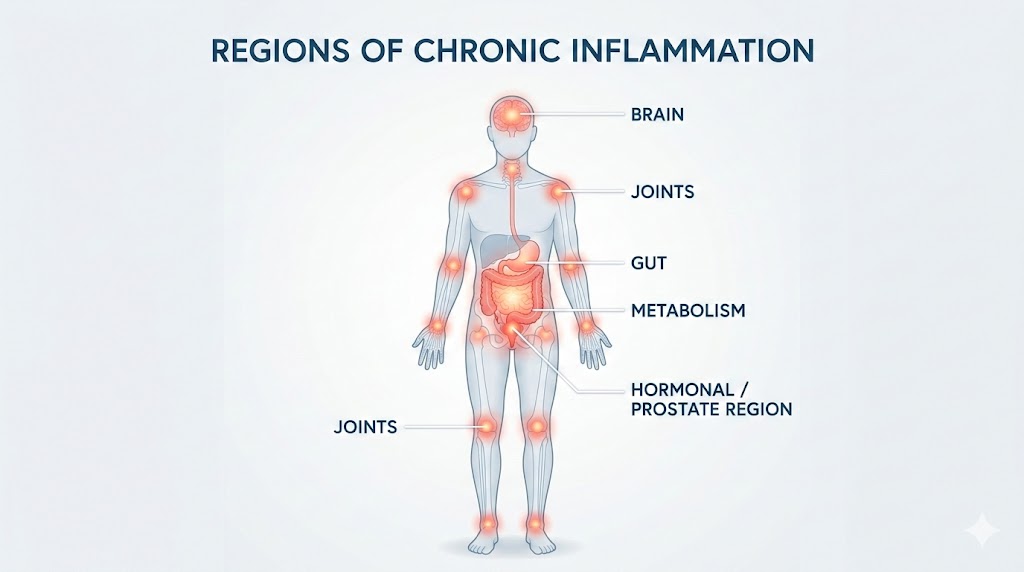
How Chronic Inflammation Affects the Body
Chronic inflammation is systemic, not localized.
🦴 Joints & Muscles
Leads to stiffness, chronic aches, slower recovery, and degenerative pain.
👉 Explore Joint & Muscle Inflammation
⚡ Metabolism & Weight
Promotes fat storage, insulin resistance, and metabolic slowdown.
🧠 Brain & Mood
Drives neuroinflammation linked to brain fog, anxiety, and memory decline.
🦠 Gut & Immunity
Triggers food sensitivities, bloating, and immune overload.
🧬 Hormones & Prostate
Suppresses testosterone, worsens urinary symptoms, and disrupts hormonal balance.
Why Chronic Inflammation Is So Hard to Detect
- Standard blood tests often miss low-grade inflammation
- Symptoms appear gradually
- Pain may be absent in early stages
- Doctors often treat outcomes, not root causes
This is why chronic inflammation is sometimes called “the silent driver of disease.”
How to Reduce Chronic Inflammation Naturally
There is no single “anti-inflammatory fix.” Real improvement comes from system-level correction.
Core Principles
- ✔ Stabilize blood sugar
- ✔ Reduce nervous system overload
- ✔ Repair gut integrity
- ✔ Support hormonal balance
- ✔ Remove inflammatory food triggers
Each system must be addressed together — not in isolation.
❓ FAQs: Chronic Inflammation
1. Can chronic inflammation exist without pain?
Yes. Fatigue, brain fog, and weight gain often appear first.
2. Is chronic inflammation reversible?
Yes, when underlying drivers are addressed consistently.
3. Does inflammation increase with age?
Yes, due to metabolic and hormonal changes.
4. Can inflammation block weight loss?
Absolutely. It interferes with insulin and fat-burning signals.
5. Is inflammation linked to anxiety and depression?
Yes, neuroinflammation affects neurotransmitter balance.
6. Do anti-inflammatory diets really work?
They help when paired with lifestyle and metabolic support.
7. How long does it take to reduce inflammation?
Weeks for symptom relief; months for deeper repair.
8. Are supplements required?
They’re optional, not mandatory — foundation comes first.
9. Why don’t doctors always detect inflammation?
Low-grade inflammation often evades standard tests.
10. What’s the biggest hidden trigger?
Chronic stress combined with blood sugar instability.
Want to Fix the Root Cause of Chronic Symptoms?
Chronic inflammation can quietly drive joint pain, fatigue, brain fog, weight gain, digestive issues, and hormone imbalance. Explore the full hub to understand the root causes — and the most effective natural support strategies.
Tip: If you’re not sure where to start, begin with the “Chronic Inflammation Guide” inside the hub.
Explore Chronic Inflammation by Body System
Chronic inflammation affects the entire body. Use the guides below to understand how it shows up — and how to address it at the root.