After giving birth, your body undergoes immense hormonal shifts — from estrogen and progesterone drops to immune system recalibration.
For many women, this transition also affects the thyroid gland, the small but mighty organ that regulates metabolism, mood, and energy.
If you’ve felt unusually exhausted, anxious, or unable to lose pregnancy weight months after delivery, your thyroid may be out of balance.
This guide explains postpartum thyroid changes, how to recognize warning signs, and what you can do to restore energy and hormonal harmony.
💠 Understanding the Postpartum Thyroid Shift
During pregnancy, your thyroid works overtime to support both you and your developing baby.
After birth, as hormone levels rapidly decline, the thyroid may become overactive (hyperthyroid) for a short time — then swing to underactive (hypothyroid) later.
This temporary condition, known as postpartum thyroiditis, affects roughly 5–10% of women within the first year after delivery.
🔄 What Is Postpartum Thyroiditis?
Postpartum thyroiditis is an inflammation of the thyroid gland that occurs after childbirth, usually within 2–6 months postpartum.
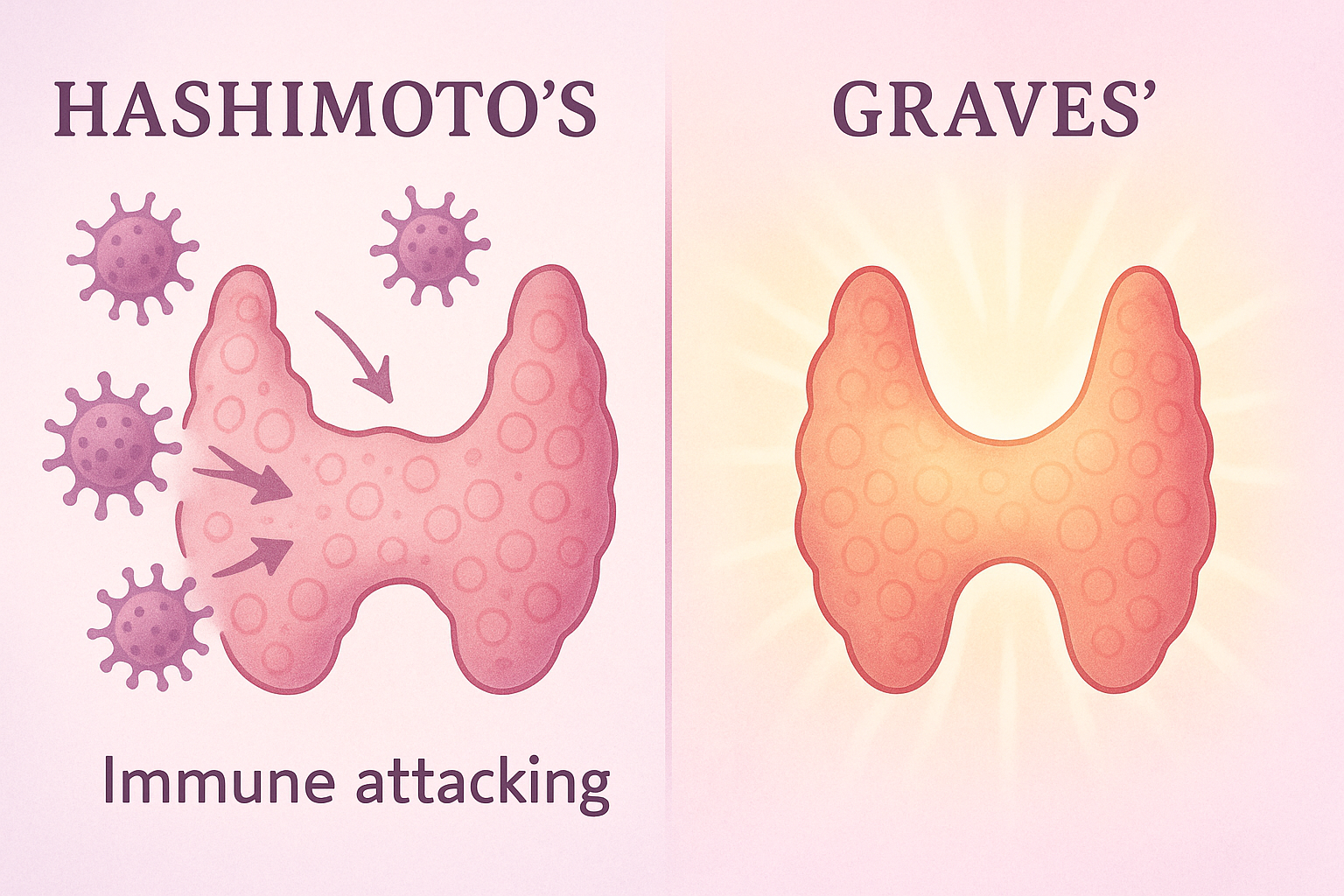
It’s believed to be triggered by immune system reactivation, where antibodies temporarily attack thyroid tissue.
Typical Phases:
| Phase | Timeline | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Hyperthyroid Phase | 1–3 months postpartum | Thyroid releases too much hormone due to inflammation. |
| Hypothyroid Phase | 3–8 months postpartum | Hormone levels drop as the gland becomes depleted. |
| Recovery Phase | 9–12 months postpartum | Thyroid often returns to normal function (but not always). |
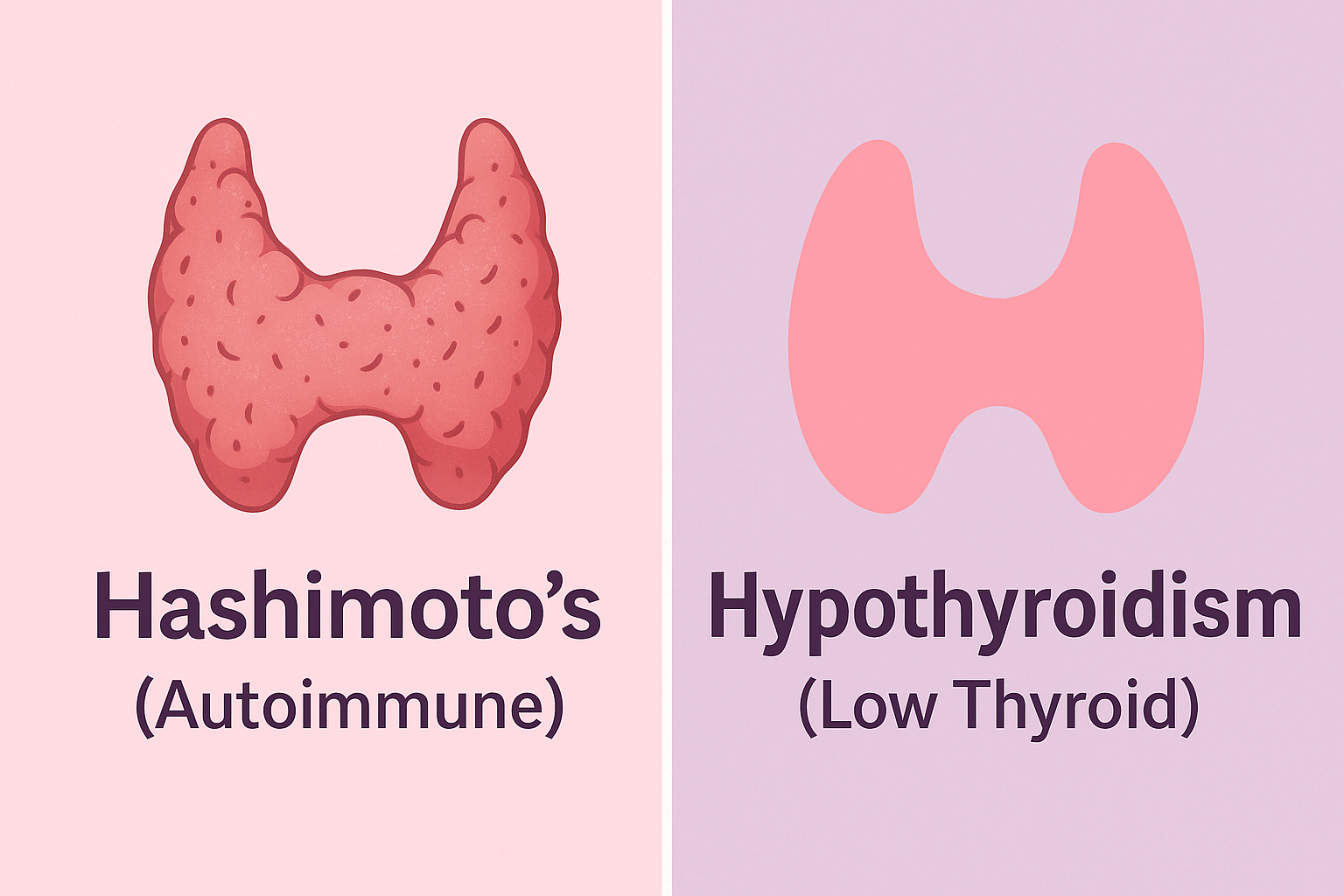
Some women recover fully; others develop permanent hypothyroidism, especially if they already had thyroid antibodies or autoimmune conditions like Hashimoto’s.
⚠️ Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Because postpartum symptoms can mimic “normal new-mom fatigue,” thyroid changes often go unnoticed.
Here’s how to tell the difference:
🔹 Hyperthyroid Phase Symptoms:
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations
- Feeling anxious or jittery
- Unexplained weight loss
- Increased sweating or heat intolerance
- Tremors or insomnia
🔹 Hypothyroid Phase Symptoms:
- Persistent fatigue
- Weight gain or fluid retention
- Hair loss or dry skin
- Depression or “baby blues” that persist
- Constipation and slow metabolism
If you’re unsure which phase you might be in, testing thyroid hormone levels can clarify the picture.
🧠 Why Postpartum Thyroid Changes Happen
- Immune Rebound Effect:
During pregnancy, your immune system naturally suppresses to protect the baby. After birth, it rebounds — and in some women, mistakenly attacks the thyroid. - Hormonal Shifts:
The rapid drop in estrogen and progesterone affects thyroid hormone binding and liver metabolism.
See: The Connection Between Estrogen Dominance and Thyroid Issues. - Nutrient Deficiencies:
Iron, selenium, zinc, and iodine are often depleted during pregnancy and breastfeeding, impacting thyroid hormone production.
Learn more in 10 Essential Vitamins and Minerals for a Healthy Thyroid. - Stress and Sleep Deprivation:
Chronic stress and lack of rest elevate cortisol, which suppresses thyroid function.
Related read: Balancing Thyroid and Adrenal Fatigue Naturally.
🩺 Testing and Diagnosis
If you suspect postpartum thyroiditis, ask your healthcare provider for a comprehensive thyroid panel:
- TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone)
- Free T3 and Free T4
- Thyroid Antibodies (TPOAb, TGAb)
- Reverse T3 (to assess conversion issues)
Regular testing every 8–12 weeks postpartum can catch fluctuations early.
🌿 Natural Ways to Support Thyroid Recovery
1. Replenish Key Nutrients
Focus on foods rich in:
- Selenium: Brazil nuts, tuna, turkey
- Zinc: Pumpkin seeds, beef, eggs
- Iron: Grass-fed red meat, spinach
- Iodine: Seaweed, iodized salt (if tolerated)
2. Support Liver Detox
The liver clears excess hormones and inflammation byproducts.
Eat cruciferous vegetables and hydrate well.
See: Foods That Harm Thyroid Health (and What to Avoid).
3. Prioritize Rest and Stress Relief
Even small steps matter — power naps, breathing exercises, or short walks.
Stress management helps restore progesterone and thyroid balance.
4. Consider Gentle Supplement Support
If fatigue and low mood persist, discuss thyroid-supporting formulas.
Guide: How to Choose the Right Thyroid Supplement for You.
🤱 Postpartum and Breastfeeding: Is Treatment Safe?
Most women with mild thyroiditis don’t require medication — symptoms often resolve naturally.
However, in more severe hypothyroid phases, your doctor may recommend low-dose levothyroxine, which is safe for breastfeeding.
Always consult your healthcare provider before starting or adjusting supplements or medications while nursing.
🌸 When to Seek Medical Advice
See your doctor if you experience:
- Unexplained anxiety, heart palpitations, or weight loss
- Ongoing fatigue despite adequate sleep
- Depression lasting more than 2 weeks postpartum
- Significant hair loss or cold intolerance
Early detection and care can prevent long-term thyroid damage and help you feel like yourself again.
🪷 Final Thoughts
Postpartum thyroid changes are common but often overlooked.
Understanding your body’s hormonal rhythm after pregnancy can make recovery smoother and prevent months of confusion or exhaustion.
By testing early, nourishing your body, and supporting your thyroid naturally, you’ll be better equipped to restore energy, mood, and well-being during this important chapter of motherhood.
Rebuild Your Thyroid Health After Pregnancy
Discover gentle, nutrient-based ways to restore thyroid function, balance hormones, and regain energy after childbirth.
Explore Thyroid Support Options →❓ FAQs
- What is postpartum thyroiditis?
It’s an inflammation of the thyroid that occurs after childbirth, often causing an initial hyperthyroid phase followed by hypothyroidism. - When does postpartum thyroiditis usually appear?
Typically between 2–6 months after delivery. - What causes thyroid changes after pregnancy?
Immune rebound, hormonal shifts, nutrient depletion, and stress contribute to temporary thyroid imbalance. - How long do postpartum thyroid symptoms last?
Most resolve within 12 months, though some women develop lasting hypothyroidism. - What are the symptoms of postpartum thyroid imbalance?
Fatigue, anxiety, weight changes, hair loss, mood swings, and slow metabolism. - Can postpartum thyroiditis affect breastfeeding?
Mild cases usually don’t interfere with breastfeeding, and thyroid medication is generally safe if prescribed. - How is postpartum thyroiditis diagnosed?
Through thyroid function tests (TSH, Free T3, Free T4) and antibody testing (TPOAb, TGAb). - Can postpartum thyroiditis turn into permanent hypothyroidism?
Yes, especially in women with existing thyroid antibodies or autoimmune history. - How can I support thyroid recovery naturally?
Prioritize nutrient-rich foods, rest, stress management, and liver detoxification. - Should I continue thyroid medication after symptoms improve?
Only under medical guidance. Some women can taper off once hormone levels normalize.
🔗 Related Articles
- The Connection Between Estrogen Dominance and Thyroid Issues
- How to Choose the Right Thyroid Supplement for You
- Balancing Thyroid and Adrenal Fatigue Naturally
- Morning Habits That Support a Healthy Thyroid
Gentle Thyroid Support for Postpartum Recovery
Thyrafemme is specially formulated to provide the nutritional support your thyroid needs during the postpartum period, helping restore energy and hormonal balance safely.
- Provides essential nutrients often depleted during pregnancy and breastfeeding
- Supports healthy thyroid function without harsh stimulants
- Formulated with women’s unique hormonal needs in mind