When it comes to heart health, few nutrients are as essential — or as misunderstood — as omega-3 fatty acids.
These healthy fats are famous for supporting brain and joint health, but research shows they also have powerful effects on blood pressure, inflammation, and artery function.
In this article, we’ll explore the role of omega-3s in blood pressure control, how they work inside your body, the best sources, and what dosage offers the greatest benefits.
(Related Reading: The Complete Guide to Lowering Blood Pressure Naturally)
🧬 What Are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
Omega-3s are essential fatty acids, meaning your body can’t make them on its own — you must get them through food or supplements.
There are three main types:
- ALA (Alpha-linolenic acid) — found in plants like flaxseed and walnuts.
- EPA (Eicosapentaenoic acid) — found in fish; reduces inflammation.
- DHA (Docosahexaenoic acid) — vital for heart and brain function.
EPA and DHA are the active forms most beneficial for blood pressure and cardiovascular health.
❤️ How Omega-3s Help Lower Blood Pressure
Omega-3 fatty acids work through several key mechanisms:
- Relaxing blood vessels (vasodilation): They improve endothelial function — allowing arteries to expand and improve blood flow.
- Reducing inflammation: Chronic inflammation stiffens blood vessels; omega-3s lower inflammatory markers like CRP.
- Decreasing blood viscosity: They make the blood “flow smoother,” reducing resistance in the arteries.
- Regulating heart rhythm: Omega-3s stabilize heartbeat and reduce risk of arrhythmias.
💡 Science says:
A 2022 meta-analysis published in Journal of the American Heart Association found that taking 2–3 grams of EPA and DHA per day lowered systolic blood pressure by 4 mmHg and diastolic by 2 mmHg on average — with even greater results in people over 45 or those with hypertension.
(Also read: Can Supplements Really Lower Blood Pressure?)
⚕️ The Link Between Omega-3 Deficiency and Hypertension
Low omega-3 levels are associated with:
- Increased inflammation
- Stiffer arteries
- Elevated triglycerides
- Slower heart recovery rate
In fact, people with low omega-3 status are up to 35% more likely to develop high blood pressure or heart disease.
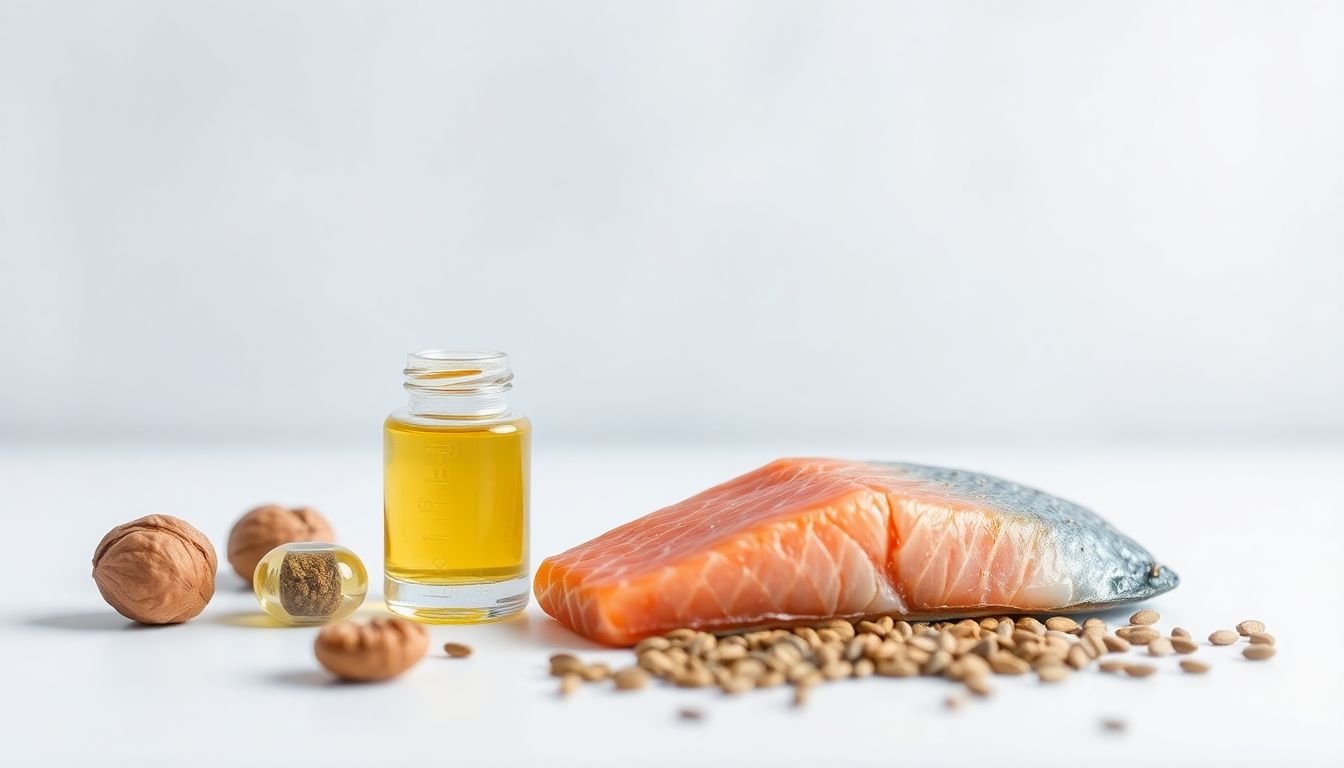
🥗 Best Food Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
The best way to boost your omega-3 intake is through a mix of diet and supplementation.
🐟 Top dietary sources include:
- Salmon
- Mackerel
- Sardines
- Anchovies
- Chia seeds
- Walnuts
- Flaxseed oil
(Also read: 10 Foods That Help Lower Blood Pressure Naturally)
💊 Omega-3 Supplements: What to Look For
If you don’t eat fish regularly, supplements are an excellent alternative.
✅ Choose high-quality omega-3 supplements that:
- Contain EPA + DHA (not just ALA)
- Provide at least 1000–2000 mg total omega-3s daily
- Are molecularly distilled to remove heavy metals
- Include vitamin E to prevent oxidation
💡 Tip: Take your omega-3s with a meal containing fat to improve absorption.
(Also read: The Best Vitamins for Heart and Blood Pressure Health)
🧠 Omega-3s, Cholesterol, and Heart Function
Omega-3 fatty acids improve the entire cardiovascular picture — not just blood pressure.
They help:
- Lower triglycerides
- Raise HDL (“good”) cholesterol
- Reduce arterial plaque buildup
- Support smoother heartbeat patterns
Combined with nutrients like CoQ10 and magnesium, omega-3s enhance energy production in heart cells and keep circulation strong.
(Also read: The Role of CoQ10 in Blood Pressure and Heart Health)
🧘♀️ Omega-3s and Stress
Chronic stress increases cortisol, which tightens arteries and raises blood pressure.
Omega-3s help regulate this by balancing stress hormones and promoting a calmer nervous system.
(Also read: How Stress Affects Blood Pressure (and Natural Remedies That Work))
🕒 How Long Before You Notice Results
It typically takes 4–12 weeks of consistent omega-3 intake to see measurable improvements in blood pressure, energy, and overall heart function.
(Learn more: How Long Do Natural Remedies Take to Lower Blood Pressure?)
❓ FAQs — The Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Blood Pressure Control
Can omega-3s really lower blood pressure?
Yes. Multiple studies confirm their ability to reduce systolic and diastolic pressure.
Which omega-3 is best — EPA or DHA?
Both are important; EPA helps with inflammation, DHA supports heart rhythm and vessel health.
How much omega-3 should I take daily?
1,000–2,000 mg combined EPA + DHA is ideal for blood pressure benefits.
Can omega-3 supplements replace medication?
No, but they can support natural control and complement your doctor’s plan.
Are plant-based omega-3s as effective?
Not as much — ALA from plants must convert to EPA/DHA, and conversion is limited.
When should I take omega-3 supplements?
With meals containing fat, preferably breakfast or lunch.
Are there side effects?
Rare and mild — sometimes fishy aftertaste or mild stomach upset.
Can I take omega-3 with CoQ10 or magnesium?
Yes, they work synergistically to support heart health.
Can omega-3s help anxiety and stress?
Yes, research shows omega-3s support mood and reduce cortisol levels.
Do omega-3 supplements thin the blood?
Slightly, so consult your doctor if you take anticoagulants.
❤️ Final Thoughts
Omega-3 fatty acids are one of the most scientifically proven natural ways to support blood pressure and heart health.
They relax arteries, reduce inflammation, and energize your heart — all without harsh side effects.
If you don’t eat fish regularly, consider adding a high-quality omega-3 supplement to your daily routine — your heart will thank you.
(Also read: Best Natural Supplements to Lower Blood Pressure)