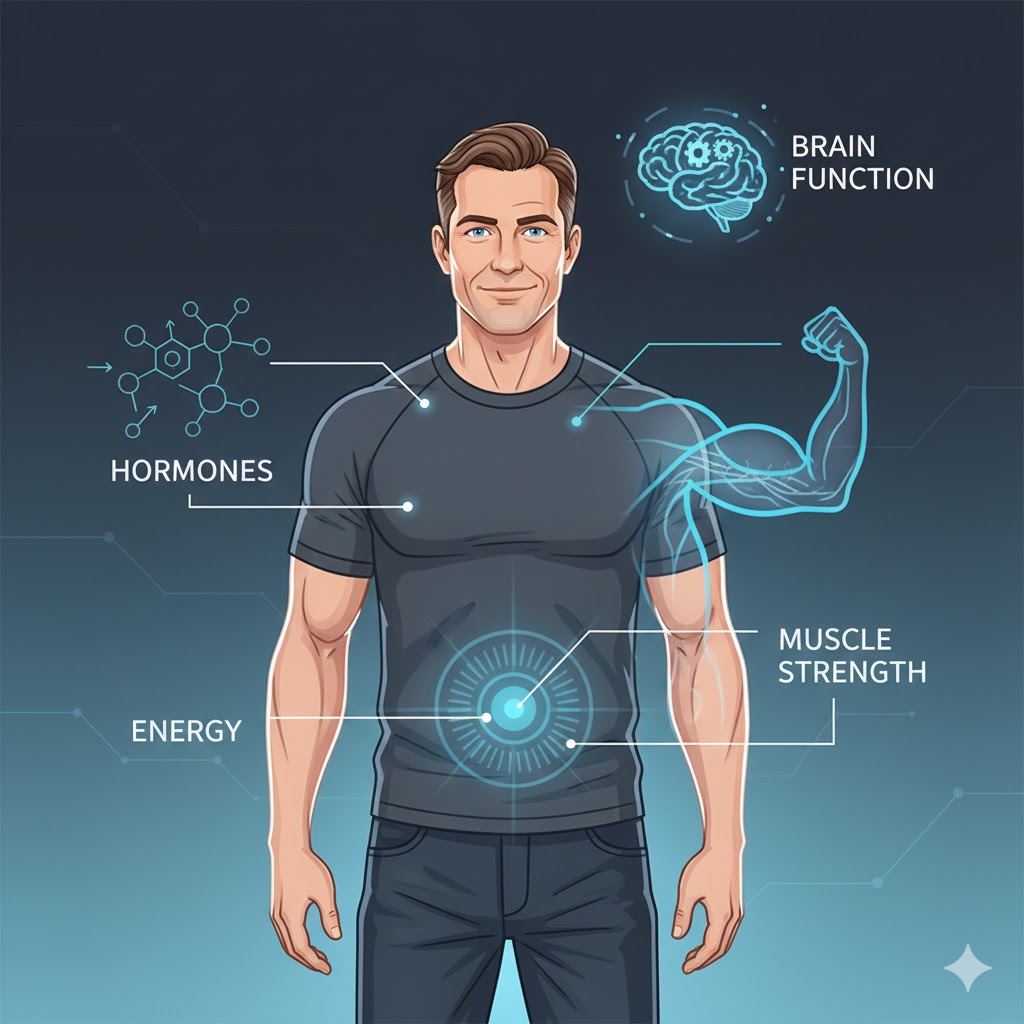
Testosterone is one of the most important hormones influencing men’s health, yet it is also one of the most misunderstood. While often associated with muscle and masculinity, testosterone plays a much broader role in energy levels, fat metabolism, mood, motivation, brain function, bone density, sexual health, and overall vitality.
This comprehensive guide explains what testosterone does, how to recognize signs of imbalance, how testing works, and the most effective natural ways to support healthy testosterone levels—all based on evidence, not hype.
What Is Testosterone?
Testosterone is the primary androgen hormone in men, produced mainly in the testes and regulated by the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal (HPG) axis. Although women also produce testosterone in smaller amounts, it is especially critical for male physiology.
Testosterone levels fluctuate naturally throughout the day, peaking in the morning and gradually declining by evening. Levels also change across the lifespan, with a slow decline typically beginning in the late 30s or early 40s.
What Testosterone Does in the Body
Testosterone affects multiple systems simultaneously, which is why low levels can cause a wide range of symptoms.
Key functions include:
- Supporting lean muscle mass and physical strength
- Regulating fat storage and metabolic health
- Influencing motivation, confidence, and mood
- Supporting focus, memory, and cognitive drive
- Maintaining bone density and joint health
- Supporting libido and reproductive function
- Assisting red blood cell production
Because testosterone interacts with other hormones—such as cortisol, insulin, estrogen, and thyroid hormones—imbalances rarely exist in isolation.
Signs and Symptoms of Low Testosterone
Low testosterone does not present the same way in every man. Symptoms often develop gradually and may be mistaken for normal aging, stress, or burnout.
Physical Symptoms
- Loss of muscle mass or strength
- Increased body fat, especially abdominal fat
- Persistent fatigue or low stamina
- Slower recovery after exercise
Mental and Emotional Symptoms
- Brain fog or difficulty concentrating
- Reduced motivation or drive
- Mood changes, irritability, or low confidence
Sexual Health Symptoms
- Reduced libido
- Changes in sexual performance or satisfaction
Experiencing one symptom alone does not necessarily indicate low testosterone, but patterns across multiple areas can warrant further evaluation.
Common Causes of Low Testosterone
Testosterone levels are influenced by both internal and external factors.
Common contributors include:
- Chronic stress and elevated cortisol
- Poor or inconsistent sleep
- Excess body fat and insulin resistance
- Inadequate protein, fat, or micronutrient intake
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Overtraining with insufficient recovery
- Exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals
- Certain medications
Addressing these root causes is often more effective than focusing on testosterone alone.
Testosterone and Aging
Testosterone naturally declines with age, but the rate of decline varies significantly between individuals. Many men maintain healthy levels well into later life when lifestyle factors are optimized.
Age-related testosterone changes may affect:
- Muscle preservation
- Energy and motivation
- Cognitive sharpness
- Body composition
Supporting testosterone as men age often requires greater emphasis on sleep quality, stress management, recovery, and inflammation control.
How Testosterone Testing Works
Testosterone testing is typically done through a blood test and should be interpreted in context.
Key Testosterone Tests
- Total Testosterone: Measures overall circulating testosterone
- Free Testosterone: Measures the biologically active portion
- SHBG (Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin): Affects how much testosterone is available for use
Testing is usually most accurate when done in the early morning, and repeat testing may be recommended to confirm results.
Understanding Your Test Results
A “normal” testosterone range does not guarantee optimal function. Some men experience symptoms despite being within reference ranges, while others feel well at lower levels.
Factors that influence interpretation include:
- Age
- Symptoms
- SHBG levels
- Overall metabolic health
- Thyroid and cortisol balance
Medical decisions should always be made with a qualified healthcare professional.
Natural Ways to Support Healthy Testosterone
Before considering supplements or medical therapies, foundational lifestyle factors should be addressed.
Sleep and Recovery
Testosterone production is closely tied to deep sleep. Consistent sleep deprivation can significantly reduce levels in a short period of time.
Stress Management
Chronic stress elevates cortisol, which directly suppresses testosterone production.
Nutrition
Adequate intake of:
- Protein
- Healthy fats
- Zinc, magnesium, and vitamin D
is essential for hormone production.
Exercise
Resistance training supports testosterone, while excessive endurance training without recovery may suppress it.
Testosterone Supplements and Boosters
Testosterone boosters are designed to support natural hormone production, not replace testosterone itself.
They may help by:
- Supporting nutrient deficiencies
- Reducing stress-related suppression
- Supporting recovery and training adaptation
Effectiveness depends heavily on ingredient quality, dosage, and individual context.
To better understand this category, see:
Testosterone and Prostate Health
A common concern is whether testosterone negatively affects prostate health. Current research does not support the idea that healthy testosterone levels inherently worsen prostate conditions.
What matters most is hormonal balance, not excess.
Explore this topic in depth here:
You can also explore prostate-specific resources in the Prostate Health Hub
Testosterone, Brain Function, and Motivation
Testosterone also influences mental performance, confidence, and motivation. Low levels may contribute to reduced focus, mental fatigue, and decreased drive.
For cognitive-focused support, see:
When to Consider Medical Support
Some men may require medical evaluation if symptoms are persistent, severe, or unresponsive to lifestyle changes. Medical options such as TRT should always be considered carefully and discussed with a healthcare provider.
This guide is for educational purposes and does not replace medical advice.
Explore the Testosterone Health Hub
This pillar article is part of our broader Testosterone Health Hub, where you can explore:
- Symptoms and testing guides
- Lifestyle and training strategies
- Ingredient deep dives
- Supplement reviews
- Testosterone and aging topics
Want a Clear, Evidence-Based Plan to Optimize Testosterone Naturally?
If you’re working on energy, strength, motivation, or body composition, the biggest wins usually come from the fundamentals: sleep, stress control, training, nutrition, and smart supplement choices. Use our hub to follow a structured path—without hype.
- Low-T signs & lifestyle fixes
- Training & recovery support
- Supplements explained (evidence tiers)
- Testing & medical context (neutral)