Quitting vaping presents unique challenges that differ from traditional smoking cessation. With higher nicotine concentrations, behavioral habits intertwined with daily activities, and often starting at younger ages, breaking free from vaping requires specialized strategies. This comprehensive guide addresses the specific hurdles vapers face and provides evidence-based methods to achieve lasting freedom from nicotine addiction.
Why Quitting Vaping is Different Than Quitting Smoking
Higher Nicotine Doses
- Nicotine salt formulas in many vapes allow for higher concentrations without harshness
- 5% nicotine pods deliver the equivalent of 20+ cigarettes in nicotine content
- Faster brain absorption leads to more rapid and intense addiction
Behavioral and Social Factors
- Stealth usage enables constant, all-day nicotine maintenance
- Social normalization among younger demographics reduces perceived risk
- Hand-to-mouth habit without the natural endpoint of a finished cigarette
Psychological Dependencies
- “Cloud chasing” and flavor experimentation become hobbies
- Device customization creates emotional attachments
- Anxiety management through constant nicotine micro-dosing
“The addiction trajectory with modern vaping devices is often steeper and more intense than with cigarettes,” notes Dr. Amanda Chen, addiction specialist. “This means cessation requires both nicotine management and significant behavioral restructuring.”
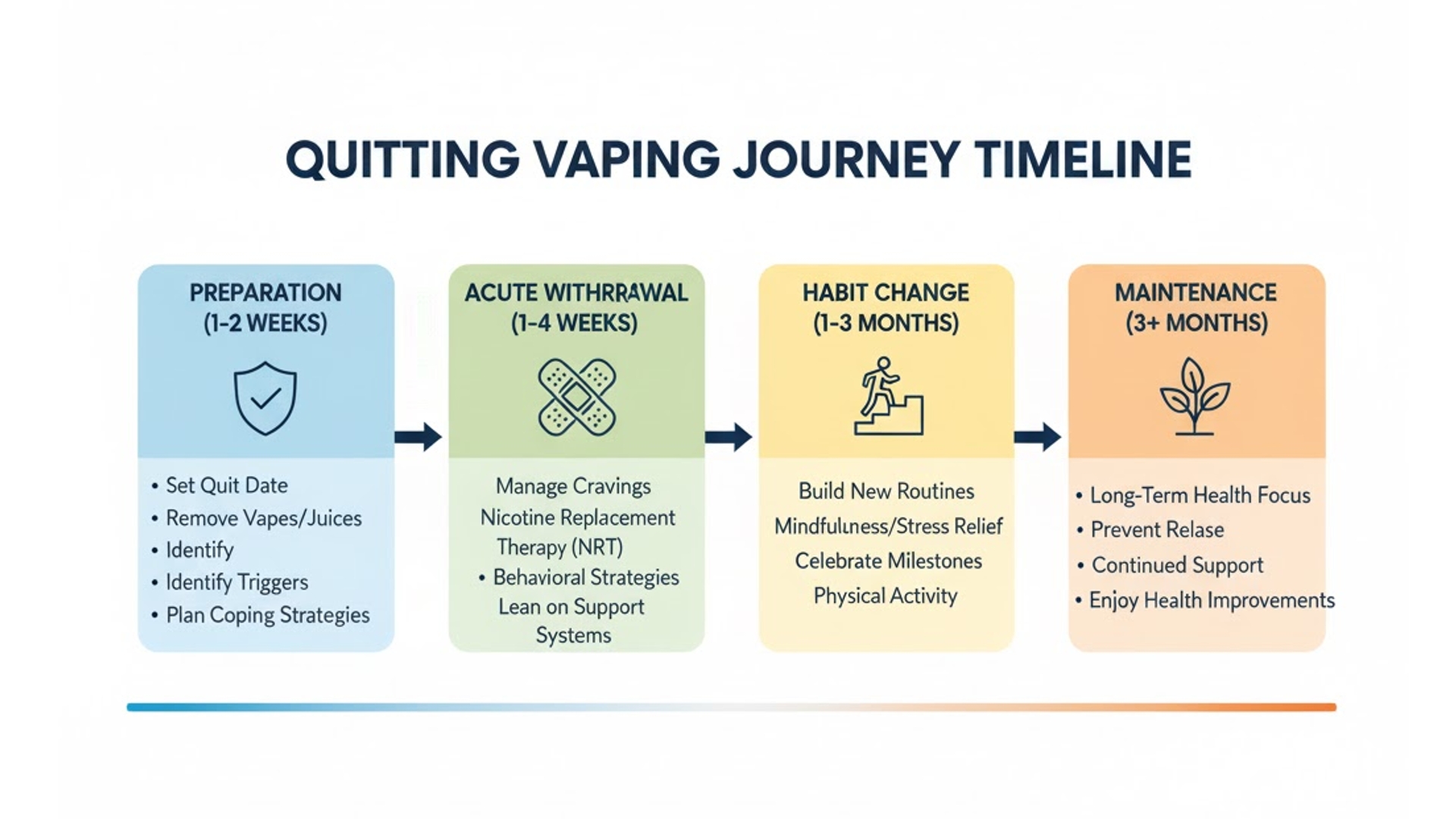
Pre-Quit Preparation: Setting Yourself Up for Success
Understand Your Triggers
Keep a vape journal for 3-7 days tracking:
- When you vape (times, situations)
- Why you vape (stress, boredom, social)
- Where you vape (specific locations, activities)
- How much you vape (puffs per session, pods per week)
Gradual Reduction Strategies
If cold turkey seems too daunting:
Nicotine Stepping:
- Switch to lower nicotine concentration pods/liquids every 1-2 weeks
- Example: 5% → 3% → 1.5% → 0% over 4-6 weeks
Device Downgrading:
- High-wattage mods → pod systems → disposable low-nicotine devices
- Reduces both nicotine and behavioral reinforcement
Usage Limiting:
- Designate vape-free times (meals, first hour awake, in bed)
- Gradually expand these windows
Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT) for Vapers
Why NRT is Crucial for Vapers
- Higher baseline nicotine levels require adequate replacement
- Different absorption patterns may need combination therapy
- Prevents relapse during intense craving periods
Effective NRT Combinations for Vapers
Option 1: Patch + Gum/Lozenges
- 24-hour patch provides baseline nicotine
- Gum or lozenges for breakthrough cravings
Option 2: Multiple Modality Approach
- Patch for steady state
- Nasal spray for rapid craving relief
- Lozenges for oral fixation needs
Vaping-Specific NRT Considerations
- Higher starting doses often needed due to high nicotine exposure
- Longer taper periods may be necessary (12-24 weeks vs. 8-12)
- Behavioral components may require additional support
Managing Vaping-Specific Withdrawal Symptoms
Intense Nicotine Cravings
- Typically peak at 24-72 hours
- Last 2-4 weeks for most users
- Use combination NRT for adequate coverage
- Practice deep breathing techniques during cravings
“Vape Tongue” and Taste Changes
- Temporary dulling of taste buds common
- Metallic taste or altered flavor perception
- Usually resolves within 2-4 weeks
- Stay hydrated and practice good oral hygiene
Oral Fixation Challenges
- Sugar-free gum, toothpicks, or straws
- Fidget toys or stress balls
- Textured lip balm for the hand-to-mouth motion
Psychological Symptoms
- Brain fog and concentration issues (1-3 weeks)
- Irritability and mood swings (peak first week)
- Anxiety about coping without vaping
- Consider lung support supplements to reinforce positive health changes
Behavioral Strategies for Lasting Success
Habit Replacement Techniques
Instead of vaping, try:
For Stress Relief:
- Box breathing or meditation
- Quick exercise bursts (jumping jacks, push-ups)
- Cold water splash on face
For Boredom:
- Learn a hands-on skill (instrument, craft, cooking)
- Chew cinnamon sticks or ginger
- Use a worry stone or fidget cube
For Social Situations:
- Have a non-alcoholic drink in hand
- Excuse yourself briefly during intense cravings
- Practice refusal scripts (“I’m taking a break from vaping”)
Environmental Restructuring
- Remove all vaping equipment from home, car, workplace
- Clean all surfaces where you vaped to remove scent residues
- Avoid vape shops and smoking areas initially
- Use air purifiers to create fresh environments
Digital Detox
- Unsubscribe from vape-related social media and newsletters
- Delete vaping apps and shopping accounts
- Use website blockers for vape store sites during vulnerable times
Pharmaceutical Options for Difficult Cases
Prescription Medications
- Bupropion (Wellbutrin): Reduces cravings and withdrawal symptoms
- Varenicline (Chantix): Blocks nicotine effects and reduces pleasure
- Northptyline or Clonidine: Second-line options for complex cases
When to Consider Medication
- Multiple failed quit attempts with NRT alone
- Co-occurring depression or anxiety disorders
- Very high nicotine dependence (2+ pods daily)
- Consult a healthcare provider for personalized recommendations
Support Systems and Accountability
Professional Support Options
- Telehealth cessation programs specifically for vaping
- Addiction counselors familiar with vaping dynamics
- Text-based support programs (SmokefreeTXT, Truth Initiative)
Peer Support Strategies
- Quit vaping apps with social components
- Online communities of former vapers
- Accountability partners who understand the journey
Family and Friend Education
- Explain vaping-specific challenges to your support system
- Request specific help (not buying devices, encouraging alternatives)
- Establish boundaries around vaping discussions
Navigating Relapse and Building Resilience
Common Relapse Triggers for Vapers
- Alcohol consumption (disinhibits restraint)
- Social situations with other vapers
- High stress periods without coping strategies
- “Just one hit” thinking that rapidly escalates
Relapse Response Plan
If you slip up:
- Don’t catastrophize – it’s a lapse, not a failure
- Analyze the trigger and adjust your strategy
- Recommit immediately – don’t continue vaping
- Use your support system for accountability
- Consider lung detox strategies to reinforce your commitment
Tracking Progress and Celebrating Milestones
Health Improvements Timeline
- 24 hours: Carbon monoxide levels normalize
- 48 hours: Nerve endings begin regenerating (taste/smell)
- 2 weeks: Lung function begins improving
- 1 month: Withdrawal symptoms significantly decrease
- 3 months: Lung cilia largely recovered, circulation improved
- 1 year: Lung cancer risk begins decreasing
Motivational Milestones
- 1 day: First 24 hours nicotine-free
- 1 week: Physical dependence breaking
- 1 month: Significant money saved
- 3 months: New habits established
- 1 year: Transformed identity as non-vaper
Special Considerations for Different Populations
Teens and Young Adults
- Peer pressure management strategies
- Parental involvement considerations
- School-based triggers and coping methods
Long-Term Heavy Users
- Extended withdrawal management
- Gradual reduction may be more effective
- Professional support strongly recommended
Dual Users (Vaping + Smoking)
- Quit both simultaneously for best results
- Higher NRT doses often needed
- Address both behavioral patterns
When to Seek Professional Help
Consider specialized addiction treatment if you experience:
- Multiple failed quit attempts despite serious effort
- Severe depression or anxiety during withdrawal
- Co-occurring substance use disorders
- Inability to function during cessation attempts
- Persistent cravings beyond 4-6 weeks
✅ FAQ
1. Is quitting vaping harder than quitting cigarettes?
For many people, yes. The higher nicotine concentrations, constant accessibility, and behavioral integration into daily life can make vaping more challenging to quit despite the shorter history of use for many individuals.
2. How long do vaping withdrawal symptoms last?
Physical symptoms typically peak at 2-3 days and significantly improve within 2-4 weeks. Psychological cravings and habit triggers may persist for several months, gradually decreasing in intensity and frequency.
3. Can I use the same methods to quit vaping as I did for smoking?
Many principles overlap, but vaping often requires higher NRT doses, longer taper periods, and more emphasis on behavioral restructuring. The strategies for quitting smoking provide a foundation that needs vaping-specific adjustments.
4. What’s the success rate for quitting vaping?
Success rates vary widely based on method used and support systems. With comprehensive approaches (NRT + behavioral support + medication if needed), success rates of 30-40% at 6 months are achievable, similar to smoking cessation with robust support.
5. Will I gain weight when I quit vaping?
Many people experience a 5-10 pound weight gain due to increased appetite and oral fixation leading to more snacking. Planning healthy alternatives and increasing physical activity can minimize this effect.
6. How can I deal with vaping cravings at work or school?
Have a “craving kit” with sugar-free gum, water bottle, stress ball, and list of quick distraction techniques. Excuse yourself briefly if needed, and use breathing exercises discreetly at your desk.
7. Are there any apps specifically for quitting vaping?
Yes, apps like Quit Vaping, quitSTART, and This Is Quitting (from Truth Initiative) offer vaping-specific support, tracking, and community features tailored to younger users and vaping-specific challenges.
8. What should I do with my vaping devices and supplies?
Remove them completely from your environment. Consider destroying them ceremonially or giving them to someone who will dispose of them properly. Cleaning your spaces eliminates triggers.
9. How long until my lung health improves after quitting vaping?
You may notice improved breathing within 2-4 weeks, with significant lung function improvement within 3-6 months. Complete recovery timeline depends on usage duration and intensity.
10. What if I’ve tried everything and still can’t quit?
Consider comprehensive addiction treatment, which may include intensive outpatient programs, medication management, and therapy addressing underlying issues. Many people need multiple attempts and increasingly intensive support to achieve lasting success.